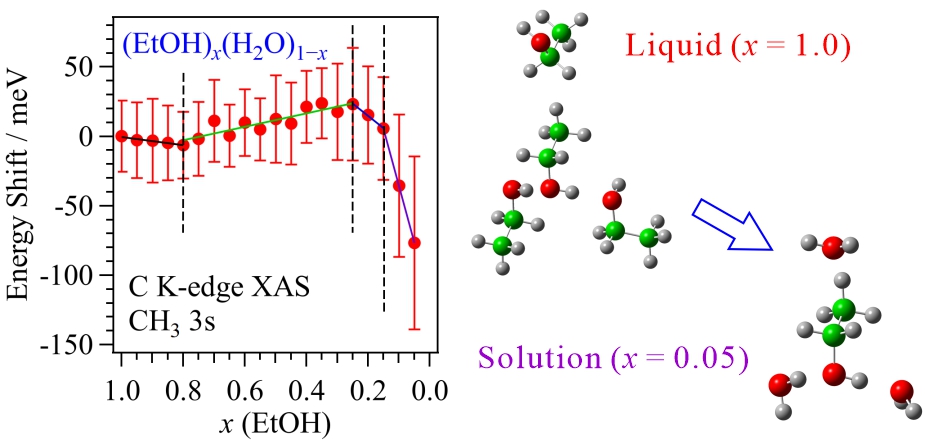
Hydrophobic cluster structures in aqueous ethanol solutions at different concentrations have been investigated by XAS. The lower energy features in the C K-edge XAS spectra arise from a transition from the terminal methyl C 1s electron to an unoccupied orbital of 3s Rydberg character, which is sensitive to the nearest neighbor intermolecular interactions. From the comparison of C K-edge XAS with the inner-shell calculations, it is found that ethanol clusters are easily formed in the middle concentration region due to the hydrophobic interaction of the ethyl group in ethanol, resulting in the enhancement of the hydrogen bond structures among water molecules.