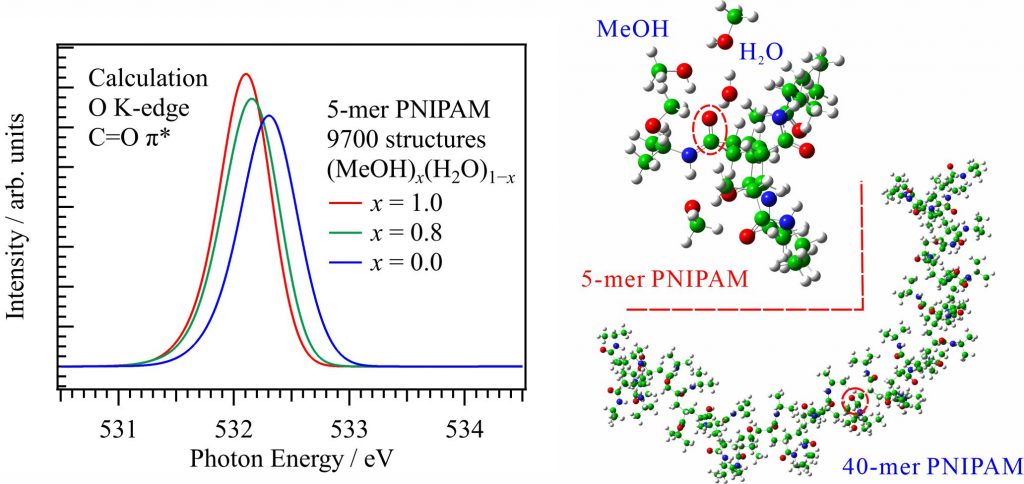
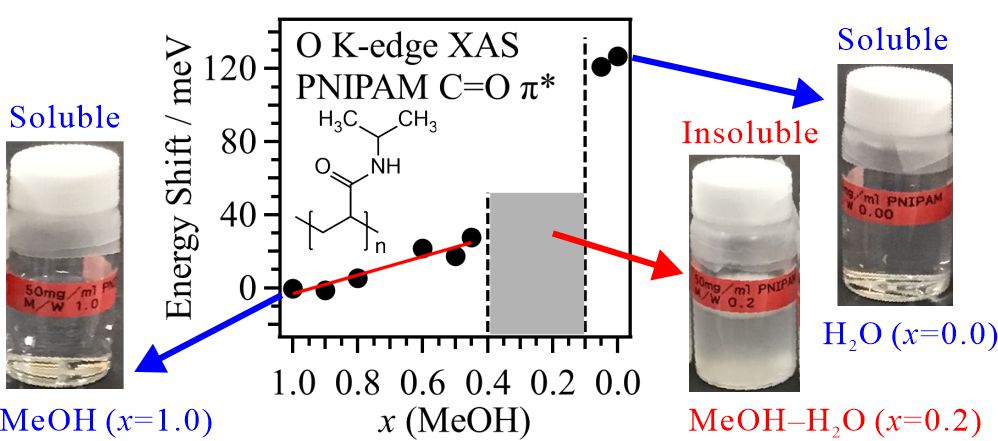
For obtaining the O K-edge inner-shell spectra of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) in solutions, the 5-mer PNIPAM chains with terminated H atoms, including the second coordination shells of the solvent methanol and water molecules, were extracted from the 40-mer PNIPAM chains in solutions, whose snapshots were obtained by the molecular dynamics simulations. The inner-shell spectra of PNIPAM in aqueous methanol solutions were obtained by averaging those of 9700 extracted polymer structures. This calculation method can be precisely evaluated the energy shifts of the C=O π* peaks of PNIPAM caused by the structural changes of the polymer chains, the substitutions of the hydrogen bonds of the C=O groups in PNIPAM from methanol to water molecules, and the increases of the coordination numbers of solvent molecules with the C=O groups, which were observed in the O K-edge XAS experiments.