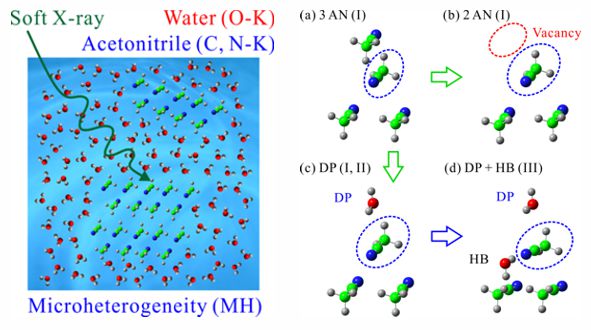
Chemical processes in solutions are influenced by microheterogeneity, where two liquids seem to be mixed in a macroscopic scale but are microscopically inhomogeneous. In aqueous acetonitrile solutions, which show microheterogeneity, molecular interactions of acetonitrile were revealed by the C and N K-edge XAS at different concentrations, and those of solvent water were separately revealed by the O K-edge XAS. The peak energy shift at the C K-edge shows three characteristic concentration regions and a phase transition-like behavior between them. The inner-shell calculations found that the dipole interaction between acetonitrile and water is the key structure to emerge microheterogeneity in the middle concentration region, which continues until the predominance of the dipole interaction over the hydrogen bond interactions.